What is an Ester?
Ester refers to an important class of chemical compounds in organic chemistry. In general, an ester is a chemical compound containing some type of functional group that a carboxylic acid (COOH) forms by combining with an alcohol (ROH). This reaction is known as esterification.
Esters are generally fragrant and flavorful compounds, so they occur naturally in many fruits and flowers and are therefore widely used in industrial applications such as perfumes, fruit flavors and sweeteners.
The structure of an ester is, in general, as follows: RCOOR', where R and R' represent carbon chains or hydrogen atoms and COO stands for the ester functional group. For example, ethyl acetate is an ester obtained by esterification of a carboxylic acid (acetic acid, CH3COOH) with ethanol (CH3CH2OH):
CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH → CH3COOCH2CH3
Ethyl acetate is an example of an ester that has a fruity odor and is used as a solvent in many industrial applications.
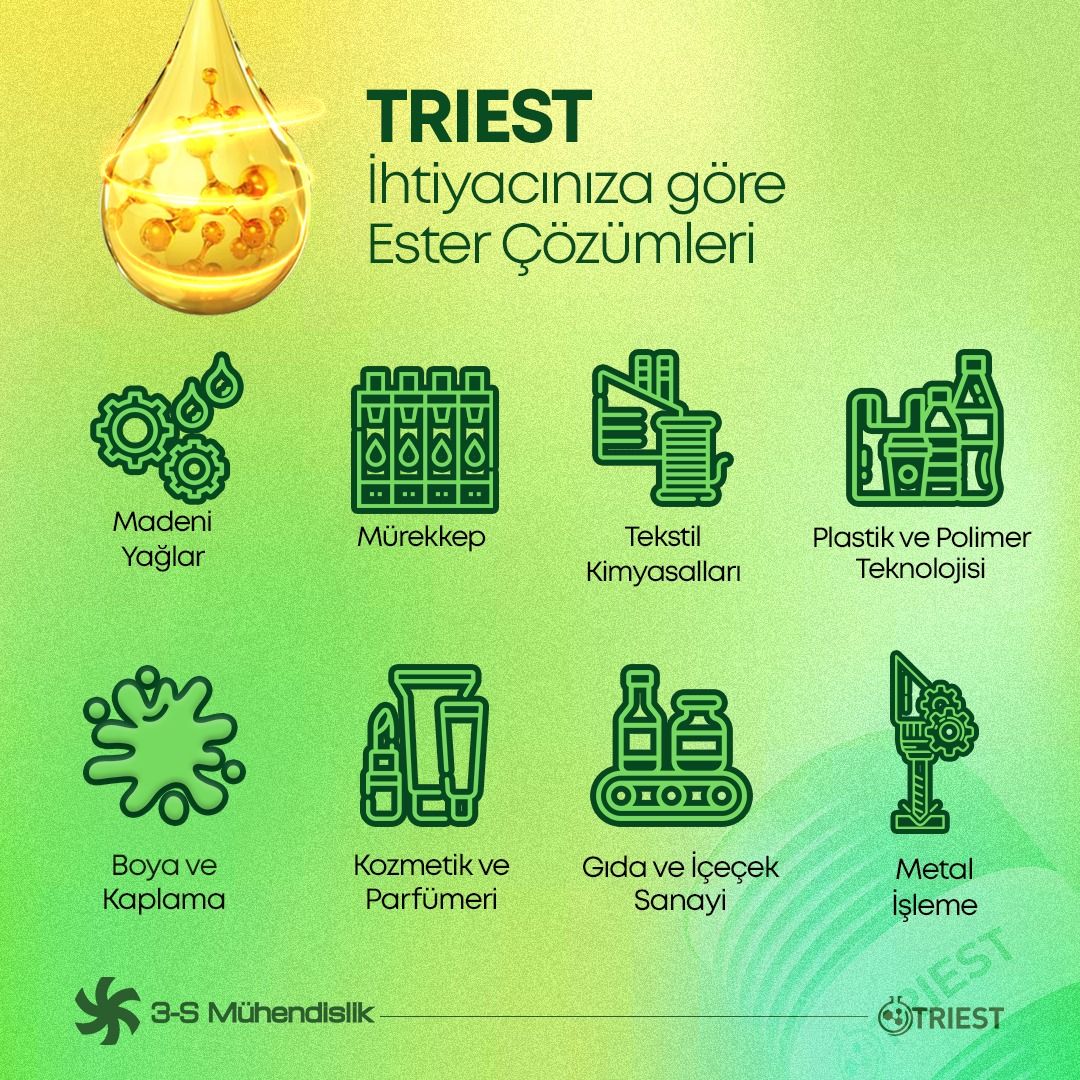
Esters offer a wide range of uses in chemistry, lubricants, metalworking, textile chemicals, cosmetics, paints, inks, food industry and many other fields.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)